Sidebar
Table of Contents
List of Tables
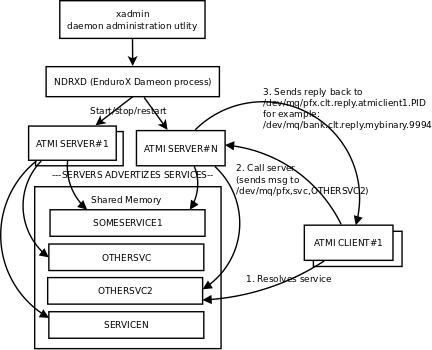
Enduro/X is middle-ware software that composes semantics of Application Transaction Monitor Interface (ATMI). Also Enduro/X provides UBF (Universal Buffer Format) so programmers can use self described buffers for inter-process communication purposes.
System principles have similarities with Oracle ® Tuxedo ® system. Enduro/X implements portions of Tuxedo FML and ATMI APIs and provides similar functionality.
Enduro/X consists release consists of various components. Like libraries for C/C++ programs, transaction monitor it self, and command line administration utility.
On each machine transaction monitor process runs locally, it controls so called server processes, which are programs which are started by transaction monitor and they advertise services. It is possible to join together many transaction monitor processes under same machine or over multiple machines. This makes a cluster.
In cluster environment services are shared over the linked local transaction monitors. It is possible to load balance some service which runs on local machine and on some other machine. The caller/client might be unaware on which machine the call actually is served.
The distribution package contains following list of resources:
Table 2.1. Distribution package description - "bin" directory
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
buildclient | Fully featured featured build client, includes static linking of XA switch |
buildserver | Fully featured server build processes, generates main with automatic advertises |
buildtms | Build alternate transaction manager, which includes statically linked XA switch |
mkfldhdr | Generates C/Go/Java header files for UBF buffers |
ndrxd | Enduro/X deamon. This process is central point of the application which does the Application Transaction Monitoring |
tmadmin | Alias for xadmin |
tpbridge | Special ATMI server which drives the connectivity for cluster purposes It allows to connect one Enduro/X instance to another Enduro/X instance |
tpevsrv | Special ATMI server which serves the local even distribution over the services |
ud | ATMI client utility. This reads stdin of dumped UBF buffer. And sends request to specified service when responses is received, it is dumped back to stdout |
xadmin | Enduro/X Administration command utility. Basically utility is also responsible for local ATMI instance start, stop, configuration test/load/reload, status printing, etc |
tmsrv | Transaction Manager Server. Responsible for XA two phase transaction management |
tprecover | Enduro/X main daemon (ndrxd) monitoring and recovery server |
tmqueue | Persistent queue support server |
cpmsrv | Client process monitor |
edb_copy, edb_dump, edb_load, edb_stat | LMDB cache management |
exencrypt | Encrypt configuration string |
exdecrypt | Encrypt configuration string |
tpadmsv | TMIB interface provider sever |
tpbrdcstsv | tpbroadcast(3) and tpnotify(3) support servers |
tpcachebtsv | Boot time cache configuration server |
tpcached | Cache management client process (house-keeping) |
tpcachesv | Interactive cache management support server (backing for xadmin commands) |
uvlog | Log file merge tool |
viewc | View file compiler |
xmemck | Memory leak monitor, used for Enduro/X debugging. |
Table 2.2. Distribution package description - "lib" directory
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
libfml.so | Dummy for compatibility |
libfml32.so | Dummy for compatibility |
libexuuid.a | UIID generation lib |
libnstd.so | Enduro/X standard library |
libubf.so | Unified Buffer Format APIs / FML support |
libatmisrvdum.so | Dummy ATMI server entries for tpsvrinit(3), tpsvrdone(3) (for Cygwin) |
libatmiclt.so | ATMI client functions (terminators for server calls) |
libatmicltbld.so | ATMI clients functions for buildclient(8) linking |
libexmemck.so | Memory usage debugger |
libndrxxaoras.so | Oracle DB static XA switch resolver library |
libndrxxaorad.so | Oracle DB dynamic XA switch resolver library |
libndrxxadb2s.so | DB2 static XA switch resolver library |
libndrxxadb2d.so | DB2 dynamic XA switch resolver library |
libndrxxawsmqs.so | Websphere MQ static XA switch resolver |
libndrxxawsmqd.so | Websphere MQ dynamic XA switch resolver |
libndrxxatmsx.so | buildclient/buildserver/buildtms statically linked XA switch resolved library |
libndrxxanulls.so | XA Null switch dummy (gives XA_OK for all XA calls) |
libcryptohost.so | Enduro/X plugin - provides configuration cryptography key from server hostname |
libnetproto.so | Enduro/X bridge protocol support lib |
libexnet.so | Enduro/X networking support lib |
libtms.so | provides transaction manager logic, used by buildtms(8) |
libndrxxaqdisk.so | TMQUEUE disk storage provider |
libndrxxaqdisks.so | TMQUEUE disk static XA Switch resolver |
libndrxxaqdiskd.so | TMQUEUE disk dynamic XA Switch resolver |
libatmi.so | ATMI common client and server shared library, serves functions like tpcall(), tpforward(), etc. |
libatmisrvinteg.so | ATMI Server process shared library - provides _tmstartserver(), and ndrx_main_integra(). This is preferred entry library for ATMI servers. |
libatmisrv.so | ATMI Server process shared library - library with build-in main() function for server process. Searches for external tpsvrinit() and tpsvrdone(). |
libatmisrvnomain.so | ATMI Server process shared library - provides ndrx_main(), expects external tpsvrinit() and tpsvrdone(). |
libtux.so | Library for compatibility |
libps.so | Platform script backing lib |
libpsstdlib.so | Platform script standard lib |
Table 2.3. Distribution package description - "include" directory
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
userlog.h | User log function |
fml.h | FML emulation header |
fml32.h | FML32 emulation header |
fml1632.h | FML 16/32 emulation header |
ubf.h | Unified Buffer Format APIs |
ubfutil.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
atmi.h | ATMI interface for compatibility |
xatmi.h | ATMI interface |
pscript.h | Enduro/X internal use header, used for module binding |
exparson.h | Enduro/X internal use header, used for module binding |
ndebug.h | Enduro/X debugger interfaces |
ndebugcmn.h | Enduro/X internal use header, used by binded modules |
ndrstandard.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
nstd_shm.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
nstdutil.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
nstd_tls.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
thlock.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
exhash.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
cconfig.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
inicfg.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
nerror.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
xa.h | XA standard header |
ndrx_config.h | Enduro/X build time platform configuration flags |
sys_unix.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
sys_primitives.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
sys_mqueue.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
sys_emqueue.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
sys_svq.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
oubf.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
odebug.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
ondebug.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
onerror.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
oatmisrv_integra.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
oatmi.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
oatmisrv.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
Exfields.h | Enduro/X internal fields definitions |
Excompat.h | Enduro/X compatibility field definitions |
tpadm.h | tpadmin call interface |
evt_mib.h | Compatibility header |
view_cmn.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
exdb.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
nstopwatch.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
exthpool.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
exstring.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
Usysfl32.h | Compatibility header |
tmenv.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
tx.h | TX transactions interface API |
Uunix.h | Compatibility header |
expluginbase.h | Enduro/X plugin API |
fpalloc.h | Enduro/X internal use header for module binding |
lcf.h | Latent Command Framework API |
Basically local ATMI works by using system’s IPC facilities. Following facilities are used. by Enduro/X:
- System V IPC Semaphores
- Posix Queues
- Posix Sharded Memory
This section gives overview how Enduro/X Operates in cluster environment. Currently there can be possible 32 nodes in cluster. Enduro/X clustering utilizes TCP/IP connections to join local Enduro/X instances. For each link between two different instances seperate TCP/IP channel is used.
Cluster can be configured in different way, for example with one central node which will have links to all other nodes. Or with no central node, then there should be created links for each of the machine pair.
Cluster with central node:
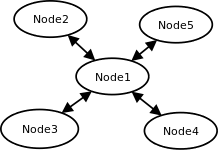
Note that in case of central node, each node only sees center node (Node1), However centre node sees all other nodes.
Cluster can consist with/out central node, for example this 5 node cluster could look like:
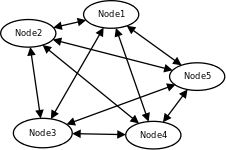
In this case each node sees other each other node and it can create invocations of the services from that node.
Cluster also can consist of mixed node. i.e. when some nodes sees each other but some nodes sees only one or few other nodes. For example consider this 7 node cluster:
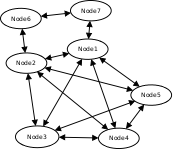
In this case Node6 and Node7 sees only few other cluster nodes. Also in this case only Node1 will see Node7 and Node2 will see Node6.
Service tables are replaced only over the direct link. They are not distributed over the whole cluster.
Local Enduro/X instances can be cluster by using special ATMI server tpbridge. This server accepts configuration (in <appopts>) where it says either this endpoint is passive (waits for connection) or active (tries to connect to specified ip address:port). The Node ID of other endpoint and some other parameters.
When connection is established, both endpoints exchanges will full service listings. When some service is remove from local instance, then over this tcp/ip link update message is sent to other node so that service is removed there too.
Full service lists are exchanged periodically (every 30 sec for example). Also tpbridge periodically sends zero length messages to other node to keep the connection open.
If connection is lost, both Enduro/X local instances will remove all other instance (who’s link is lost) services from shared memory.
Here is complete scheme how two nodes cooperate:
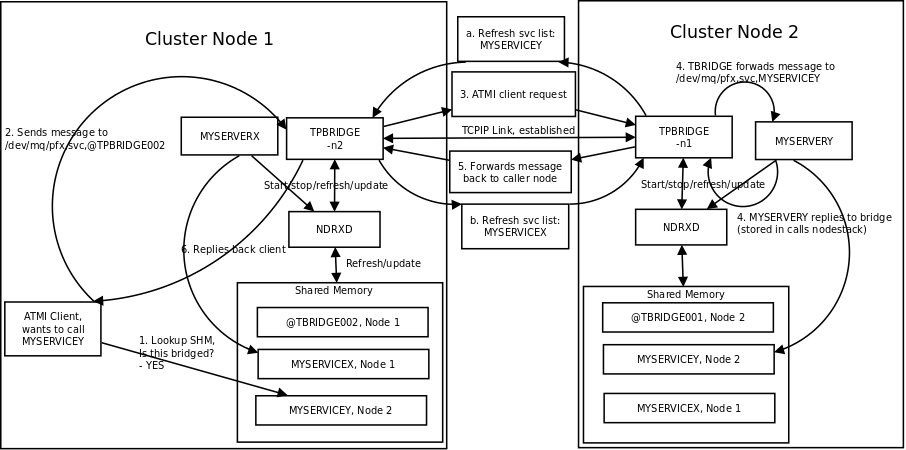
As you see firstly when TCP connection is established, service lists are exchanged in points a. and b. (also nodes exchange clock diff so that each call duratation can be corrected between nodes). Each ndrxd instance updates shared memory of services received from bridge services.
After that we have ATMI client on Node1 which calls service MYSERVICEY which is located on Node2. It resolve shared memory which says that this is on other node. Then call is made to TPBRIDGE002 Queue, which forwards the packet to other node. See points 1. - 6.
Also it is possible to have service be presented locally and on remote machine. All this information is recorded in shared memory for each of the services. Each shared memory entry contains the 32 element long array which at each cell contains the number of services shared on other node. Enduro/X environment parameter NDRX_LDBAL says in percentage how much requests serve locally and how much to send to remote machine. Percentage is calculated on random basis and remote node is also calculated on random basis. The shared mem info can be looked by xadmin, psvc command, for example:
$ xadmin NDRX> psvc ndrxd PID (from PID file): 5505 Slot Service Name Nsrv Flags CSrvs TClst CMAX CNODES ------ ------------ ---- ----- ----- ----- ---- -------------------------------- 318 RETSOMEDATA 1 1 1 3 12 00000000000300000000000000000000 1051 UNIX2 1 1 1 2 12 00000000000200000000000000000000 3844 @TPEVUNSUBS 1 1 0 0 0 00000000000000000000000000000000 4629 UNIXINFO 1 1 1 3 12 00000000000300000000000000000000 8676 ECHO 1 1 1 3 12 00000000000300000000000000000000 10293 TIMEOUTSV 1 1 1 3 12 00000000000300000000000000000000 11169 @TPEVSUBS 1 1 0 0 0 00000000000000000000000000000000 14301 @TPEVDOPOST 1 1 0 0 0 00000000000000000000000000000000 14894 TESTSV 1 1 1 3 12 00000000000300000000000000000000 16648 @TPBRIDGE002 1 1 0 0 0 00000000000000000000000000000000 16681 @TPBRIDGE012 1 1 0 0 0 00000000000000000000000000000000 17001 NULLSV 1 1 1 3 12 00000000000300000000000000000000 17386 @TPEVPOST 1 1 0 0 0 00000000000000000000000000000000 NDRX>
Which for example displays that 2 service instances of UNIX2 is available on Node12.
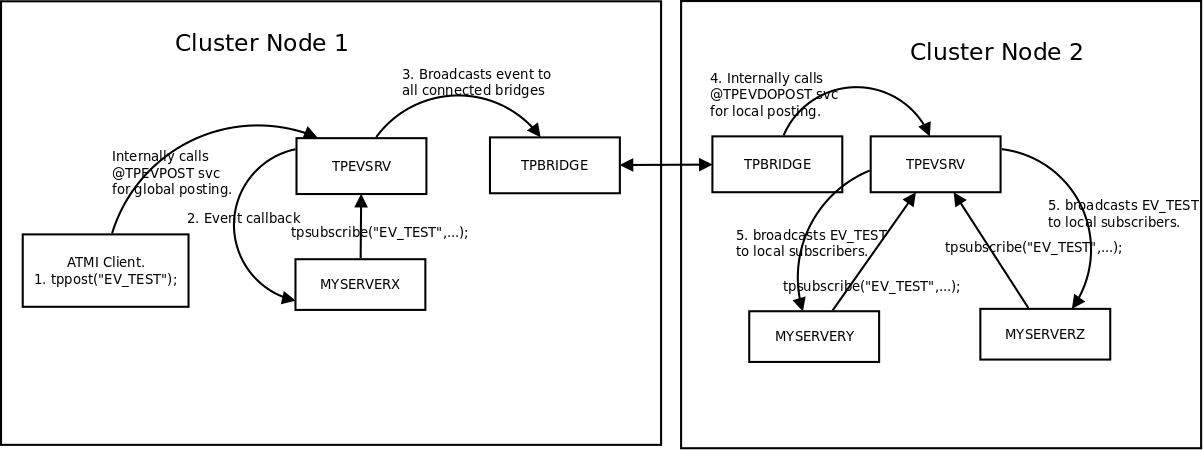
Enduro/X Supports ATMI events via tpsubscribe(), tppost() and tpunsubscribe() calls. Events are processed by special ATMI server named tpevsrv. This server ships in Enduro/X package. Events are supported in clustered environment too. In this case the local node additionally broadcasts event to all other connected nodes. On other nodes tpbridge process delivers this event to local tpevsrv which posts the event locally only.
This section lists the features of Enduro/X framework:
- Runs on 64bit GNU/Linux, starting from Kernel version 2.6.12.
- Distributed architecture.
- Peer based cluster. None of cluster nodes are master.
- PING of ATMI servers are supported. If server does not respond on pings withing timeframe, they being restarted.
Enduro/X monitors processes:
- For long startup, processes are being killed and restarted
- If proceses for some reason dies, they are being restarted
- If process dies who was the only which provides some service then SRVCERR response is sent back to caller
- For long shutdown (not in time frame), processes are forcibly killed
- The run-time is possible without local central ATMI Monitor (ndrxd). As long as other servers are running, system will work.
- It is possible to restart ndrxd during the runtime. Runtime will not be interrupted. When doing restarting, ndrxd must be started in recovery mode. In this mode it learns about the system and only after a while it becomes a master of the system.
- Local housekeeping is made. If ATMI clients are unclean shutdown (i.e. not called tpterm()). Then Enduro/X daemon detects these cases and cleans up system accordingly.
- It is easy to debug application for Enduro/X. The server processes is possible to start from command line (not mandatory started by ndrxd). This means that it is possible to start server processes via wrappers like valgrind or start via IDE and use step by step debugging of server process.
- System is tested by extensive automated unit tests. It is possible to link binaries directly with correct shared libraries.
- It is possible to specify environment overrides for each of the separate ATMI server.
- Enduro/X contains debugging facilities. It is possible to get debug logs for Enduro/X ATMI and UBF sub-systems. Logging for each of the systems can be configured separately for each of the executables using these libs.
- ATMI configuration can be reloaded during runtime. It can be done as simple as just editing the config file ndrxconfig.xml and running xadmin reload.
This section lists additional related documents.
Enduro/X Documentation
[ex_adminman] Enduro/X Administration Manual
[building_guide] Building Enduro/X On GNU/Linux Platform
[ex_devguide] Additional developer information
